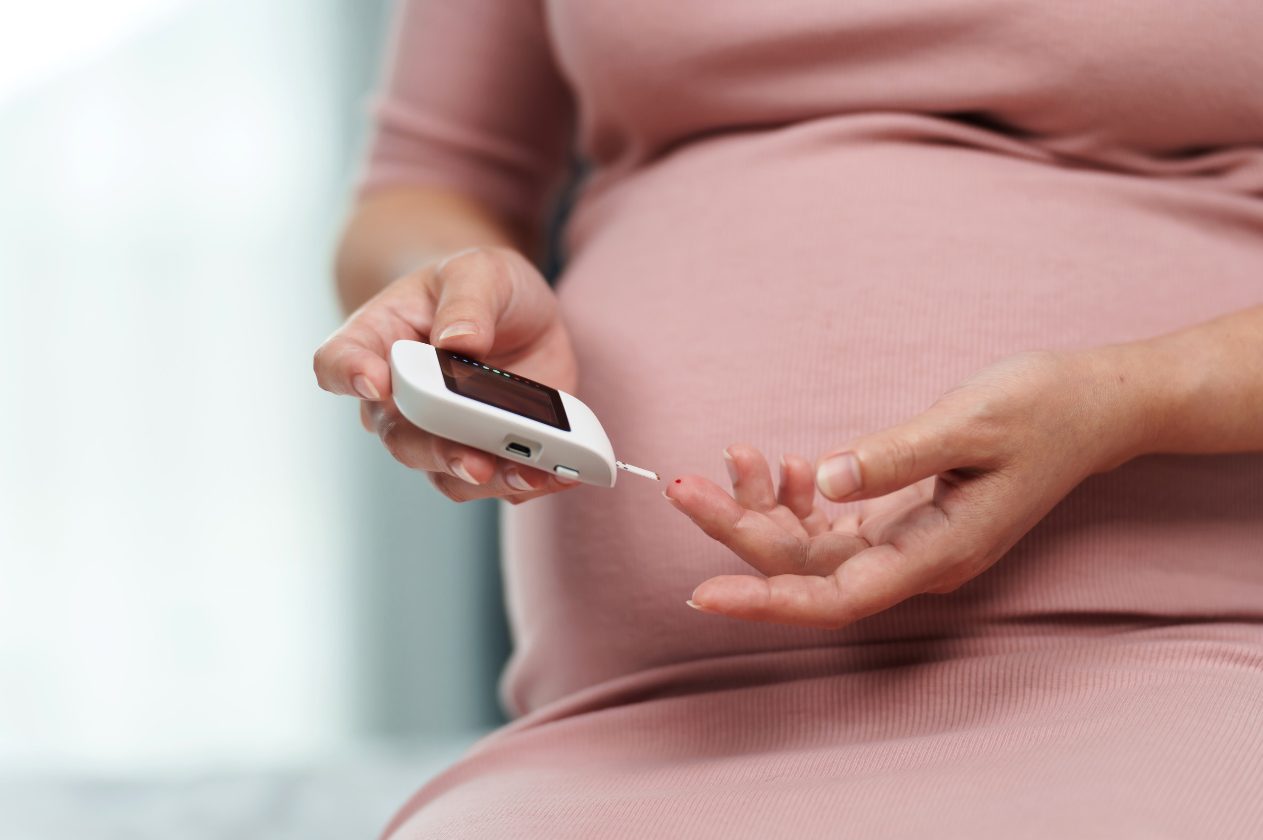
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased needs during pregnancy. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, and during pregnancy, hormonal changes can affect the body’s ability to use insulin efficiently. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which can have consequences for both the mother and the baby.
Risk Factors and Symptoms
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes, including obesity, a family history of diabetes, being over the age of 25, and having previously given birth to a baby weighing over 9 pounds. Symptoms may be difficult to notice, but common signs include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and nausea.
The Impact on Pregnancy
If gestational diabetes is not well-managed, it can lead to a range of complications. High blood sugar levels can result in:
- Preterm birth: Increased risk of early labor and delivery.
- Preeclampsia: A condition that causes high blood pressure and organ damage in the mother.
- Macrosomia: A condition where the baby grows larger than normal, which can make delivery more difficult and increase the risk of injury during birth.
- Low blood sugar in the baby: After birth, babies born to mothers with untreated gestational diabetes may experience low blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous.
Testimonies from Expecting Mothers
Sarah, 29, Mother of One
“When I found out I had gestational diabetes, I was scared. I had no idea what it meant for my baby. But after speaking to my doctor and attending a nutrition class, I learned how to manage it. I started monitoring my blood sugar, eating healthier, and exercising regularly. My baby was born healthy, and now I feel empowered knowing I can manage my health better in my next pregnancy.”
Jennifer, 34, Expecting Her Second Child
“During my first pregnancy, I had no issues, but this time I was diagnosed with gestational diabetes early on. It was tough at first, especially trying to adjust to the dietary changes, but the support from my healthcare team made a big difference. They helped me create a meal plan, and I learned how to check my blood sugar levels at home. It’s not easy, but I’m thankful that I caught it early, and I’m doing everything I can to ensure a healthy pregnancy.”
Managing Gestational Diabetes
Managing gestational diabetes requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medical monitoring, and sometimes medication. Key strategies include:
- Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regularly checking blood glucose levels helps ensure they remain within a healthy range.
- Eating a balanced diet: Focusing on whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins while limiting sugary and processed foods is essential.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, like walking or swimming, can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Medication: In some cases, insulin injections or oral medications may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that requires attention and management, but with proper care, women can have healthy pregnancies and deliver healthy babies. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and an active lifestyle are the keys to keeping blood sugar levels under control.
As Sarah and Jennifer’s stories show, while the journey may be challenging, it is possible to manage diabetes during pregnancy and ensure the health of both mother and baby.
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant and are concerned about gestational diabetes, talk to your healthcare provider for guidance on screening, prevention, and treatment.
BY SHEMA Hugue